


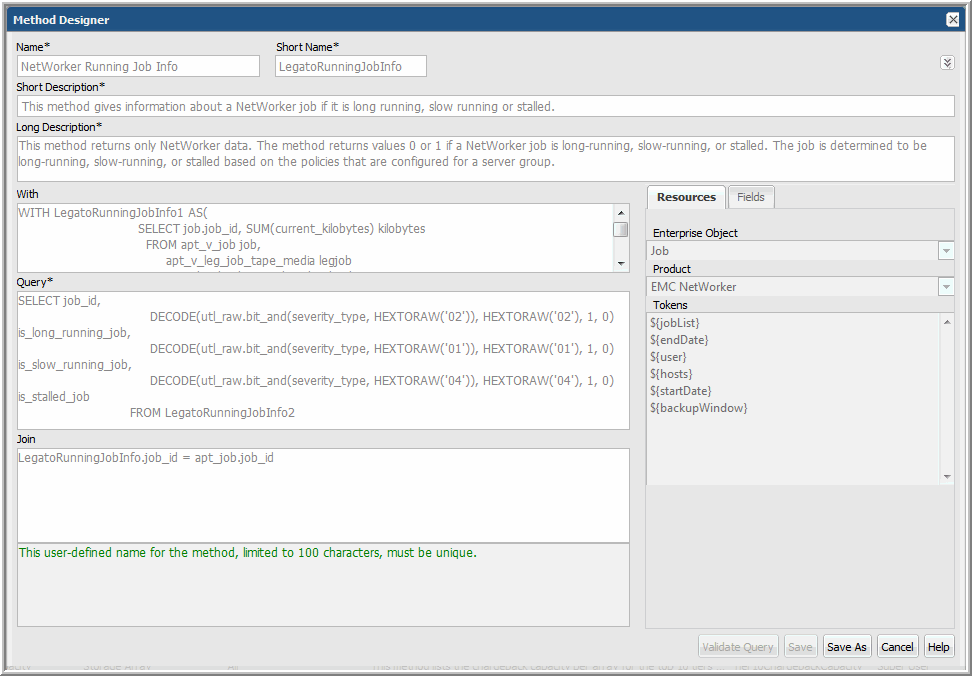
Name | This user-defined name for the method, limited to 100 characters, must be unique. |
Short Name | This user-defined, case-insensitive name must be unique, with the following constraints: • Limited to up to 23 characters. • Cannot begin with a number. • Cannot contain special characters or spaces. Use this name when defining a WITH or JOIN clause. During query validation, you may see this name listed in error messages. |
Short Description | This description, limited to 200 characters, is displayed in the methods view panel. |
Long Description | The long description is limited to 4,000 characters. Use this description to provide essential details, such as prerequisites, which will aid anyone wanting to customize the method. |
With Clause | Use the SQL WITH clause to assign a name to a subquery block so that it can be easily referenced in the query. The WITH clause must follow these rules: • WITH clause aliases must be unique across all the functions used in a report template; therefore, create an alias in the following format: <function_name><number> Example: BackupWindow1 • Cannot contain Oracle reserved words that can alter data in the database; for example, DELETE, UPDATE, or INSERT. |
Query | Define the SQL query with SELECT statements to return data from the database. • Cannot contain Oracle reserved words that can alter data in the database; for example, DELETE, UPDATE, or INSERT. • All columns in the SELECT clause must be aliased; for example, SELECT decode(client_id,1,'121212',2,'2323',5) A FROM apt_v_job • The function, collectString, can be used in the Method Designer to concatenate distinct values. The Oracle function, aptStringConcat with DISTINCT or UNIQUE, cannot be used to concatenate values in a method, even though the method will validate and save. When that method is used in a report template, it will fail. |
Join Clause | Use the SQL JOIN clause to combine results from the Method with the results of the template. The JOIN clause must follow these rules: • The JOIN conditions should use relevant enterprise object tables only. See the Dynamic Template Designer to view the table associated with a field. • Only the equal sign (=) is supported. • The method’s field should always be defined on the left side of the equal sign (=) . • SQL functions, such as UPPER, DECODE, or LOWER cannot be used in a JOIN clause. • Certain database tables cannot be used in JOIN clauses. See Exception Tables for a Method’s Join Clause. |
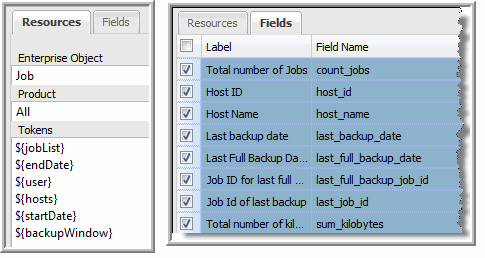
Fields | When adding a Method, the Fields pane will be populated only after the query has been successfully validated. Check the boxes to select the fields that will be available in the Dynamic Template Designer so that the method can be included in a report template. Several entries are required for each field before the method can be successfully saved. • Label: User-supplied. This label is what will appear in the Report Template. • Field Name: Pre-defined by the Method Designer. • Short Description: User-supplied. • Long Description: User-supplied. |
Resources | • Enterprise Object: Select an enterprise object—Data Domain, Host, Job, or Storage Array. This selection makes a method available to only templates created for that object. It also drives the list of tokens that are available for use in a query to enable variable substitution at report run time. • Product: Select a specific vendor product (subsystem) for the enterprise object; for example, for a storage array enterprise object, EMC VNX (Celerra). • Tokens: These tokens can be used in a query to enable variable substitution at run time. Place your cursor at the insertion point in the query and double-click the token. See Tokens for Methods. The list of relevant tokens is driven by the selected Product Group. |