Configure Host Discovery Policies to Populate the Host Inventory
Host Discovery begins with a Discovery Policy, which identifies the Data Collector that will gather information about hosts in your environment. In addition, a policy has an associated set of credentials, WMI proxies, and paths to access commands on the hosts. For additional pre-requisite details, see
Host Resources Prerequisites and Configurations and
Host Inventory Configuration Steps.
A Discovery Policy typically is used once to initially populate your host inventory. Executing a discovery policy more than once has no effect for hosts that were previously discovered. To identify and resolve connectivity issues, see
Validate Host Connectivity.
Although all hosts can be included in a single policy, you might want to create one or more Host Discovery Policies in the following recommended groupings:
• by OS (Windows or Linux) - This grouping is essential, as the probes and parameters are OS-specific.
• by common attributes, such as User ID, password, access control commands (sudo, pbrun, sesudo), PATH
• by application, such as Oracle or Exchange
Discovery Policy Considerations
If your enterprise configures hosts to lock out access after multiple failed authentication attempts, take the following tips into consideration:
• If you choose more than one credential in the Discovery Policy credentials list, you risk host authentication failure lock-out. The discovery process will try the first credentials and if they fail, discovery will try the next credentials that you’ve selected. Therefore, if your hosts are configured to prevent multiple authentication retries, multiple failed attempts may cause a lock-out.
• If multiple Discovery Policies are running simultaneously, with one policy using an IP address to access the host and the other policy using a name to access the host, the multiple access attempts may cause a lock-out. Note that if the authentication attempts are successful, only one host record is added to the inventory.
Configure a Discovery Policy
Note: A Discovery Policy typically is used once to initially populate your host inventory. Executing a discovery policy more than once has no effect for the subsequent runs for hosts that have already been discovered and added to the inventory.
For additional information about Host Inventory Discovery and Management, see:
To create/edit Host Discovery Policies, in the Storage Viewer toolbar select:
1. Select Admin > Data Collection > Host Inventory.
2. Click
Discover Hosts.
3. Click Add to configure settings and then click OK.
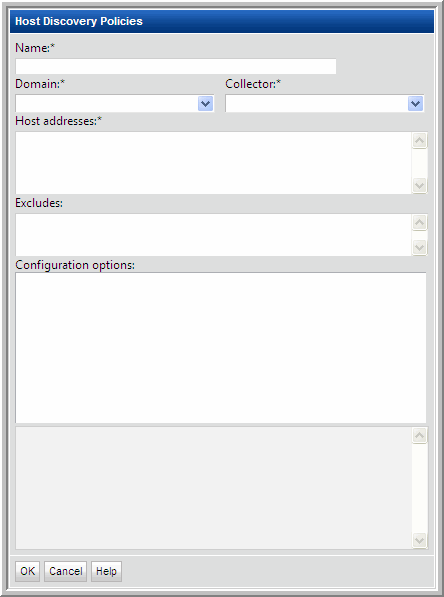
Field | Description | Sample Values |
Name* | Assign a name to identify this Discovery Policy. | |
Collector* | Select the data collector from the drop-down list | |
Domain* | Select the Storage Viewer Domain from the list; for most environments, only one Domain is displayed. Multiple domains facilitate management for Managed Services Partners (MSPs). | |
Host addresses* | • A range of IP addresses can be specified • Hostnames and/or IP addresses can be listed, separated by commas | 192.168.0.1-250 172.168.1.21, ABChost1, ABChost2, 172.168.1.58 |
Excludes | List any known IP addresses that you know are not valid for host collection; for example, the IP address of a printer. IP address ranges are also supported. | |
Configuration options | This list gets populated when you select a Domain at the top of the Host Discovery Policies window. • Credentials • WMI Proxies • Paths Expand these lists to select the configurations to be used by this Discovery Policy. IMPORTANT NOTE: If you choose more than one credential in the list, you risk host authentication failure lock-out. The discovery process will try the first credentials and if they fail, discovery will try the next credentials that you’ve selected. Therefore, if your hosts are configured to prevent multiple authentication retries, multiple failed attempts may cause a lock-out. | |